Discover the Acea Group online 2019 Sustainability Report
Context analysis and business model
CONTEXT ANALYSIS
Acea Group has an attentive and sustainable operational and economic-financial management, guided by the principles of corporate social responsibility and able to promote the development of the territories it works in. It therefore monitors the scenario of reference, thus identifying and analyzing the factors that be significant for its business, such as competitive, sustainability and regulatory areas that can affect the achievement of strategic goals. Factors outside the Group are supplemented by the context within the Group, in organizational terms and relating to energy and environmental impacts, technological innovations, development of human capital, protection of workers’ health and safety and sustainable and responsible management of the supply chain.
THE ENERGY MARKET AND COMPETITORS
THE INTEGRATED WATER SYSTEM
In the water sector, the main development driver is the progress being made in the regulation by the ARERA, which rewards the efficiency of operators. Similarly to the electrical industry, in fact, the national Authority resolved on the new regulation for the technical quality of the integrated water service starting from December 2017 using a reward/penalty mechanism linked to the compliance with performance standards (service levels) and also an automatic indemnity system for customers which is added to that already defined in relation to contractual quality. There are therefore development opportunities for the service managers that are closely linked to the capacity to adopt developed technological systems, highly efficient disclosure and organizational models, standardized and repeatable, capable of significantly affecting the improvement of performance levels.
THE WASTE MANAGEMENT MARKET
The current situation of production and treatment capacity for waste in the traditional operational areas of the Acea Group and in the neighboring areas shows a high “potential demand” for waste management (disposal in landfills, waste-to-energy, composting and biogas production, sludge and liquid waste treatment, recycling of mixed materials and production of secondary raw materials). This is facilitated by a national regulatory framework that provides incentives, by European directives on the recovery of materials and energy and by the European Union’s policy guidelines on the circular economy (closing the loop), which are being implemented at the national level by virtue of a delegated law that has given the government the obligation to update environmental standards – thus adapting it to the new EU standards – by 2020. Opportunities for developing the sector are therefore highlighted, also facilitated by the availability of new technologies (for example in composting) and by possible forms of industrial integration with other operators.
INSTITUTIONAL INVESTORS
SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT
ENVIRONMENTAL AND ENERGY IMPACTS
- Management systems: the widespread adoption of environmental and energy management systems is a concrete response on the importance of environmental dynamics for Acea and a managerial tool for continuous improvement in performance.
- Mobility management: in this context, the Acea Group has undertaken initiatives to reduce employee travel and to encourage less polluting means of transport.
- Carbon Disclosure Project (CDP): Acea publishes its initiatives, communicating them to the international CDP organization, which drafts annual online reports aimed at informing analysts and lenders about the levels achieved by companies in managing risks and opportunities related to the topic of climate change.
- Green purchases and environmental awareness development of the supply chain: Acea has set itself the goals of increasingly integrating the assessment of environmental aspects through the implementation of CAMs for the supply of compatible product categories. Moreover, it has committed to assessing its suppliers on an annual basis with regard to the environmental performance of the products/services supplied, and to inform/train contractors and subcontractors regarding the environment.
- Energy management: using energy management, Acea Group promotes the improvement of the energy performance of plants and buildings by implementing best procedures to reduce energy consumption and encourage the use of energy from renewable sources.
STANDARDS IN THE REFERENCE MARKETS AT A LOCAL, NATIONAL AND SUPRA-NATIONAL LEVEL
The regulatory context of Acea is wide-ranging and articulated according to the specificity of the businesses handled – water, energy and environment – and the variety of the frameworks within which the legal and regulatory disciplines intervene, which affect the business operations, from administrative authorization profiles to those protecting the market and competition. Added to such aspects is the peculiarity of the nature of listed Company, with the related legal impacts, for example, in terms of regulating communications to the market. The regulatory scenario is therefore analysed from a multidisciplinary viewpoint, applying a 360˚ overview and continuous interpretative analysis, in order to detect developments of particular significance, thus identifying and assessing risks and opportunities in terms of strategy and operating management. The revision of the regulatory framework governing the procurement sector, with amendments to the new Code of Public Contracts, is one of the most important issues of the year.
REGULATION OF THE SECTOR AUTHORITY
DEVELOPMENT AND TECHNOLOGICAL INNOVATION
At Acea, the Innovation, Technology & Solutions Function reports directly to the CEO and has the task of ensuring a model of innovation for the Group through the implementation of processes and approaches typical of open innovation, with the involvement of internal and external stakeholders as defined by the Industrial Plan. In this context, the dissemination of a culture of innovation has been encouraged by involving all Group employees in specific initiatives; partnerships have been established at a national and international level with the aim of strengthening Acea’s positioning in the innovation ecosystem and identifying new business opportunities; innovative solutions (proof of concept) from start-ups and SMEs have been analyzed and tested.
DEVELOPMENT OF HUMAN CAPITAL
• involvement of people in the Group’s identity;
• inclusion and organizational well-being, thus recognizing the strategic value of diversity and workers’ health and safety.
SUSTAINABLE MANAGEMENT OF THE SUPPLY CHAIN
At the service of the territory and the public, Acea is fully mindful of the virtuous partnership that can be established with the supply chain. In fact, it attributes greater value and reliability to contractors that have certified quality, environmental, safety, energy and social responsibility management systems and provides a self-assessment questionnaire on these issues for the majority of suppliers that register for qualification systems. In terms of green procurement, Acea applies the Minimum Environmental Criteria in its tender specifications and is working to extend this same approach to product categories that are not yet mentioned in the relevant Ministerial Decrees. With the aim of raising awareness and supporting the continuous improvement of the supply chain, Acea also carries out second-party checks and strict safety inspections at the construction sites. This brings to light good practices and, at the same time, identifies shared paths towards growth and improvement.
SAFETY AND HEALTH AT WORKPLACE
Acea works hard to instill a widespread safety culture, involving all its employees and the supply chain. It therefore carries out targeted awareness campaigns addressed both internally and to contractors, directly involving people, in the belief that it is necessary to set up effective tools for the prevention of accidents. For this purpose, it has also implemented an advanced risk assessment model, not to mention control and mitigation measures. Acea’s “Vision” of workplace safety – which is the prelude to the preparation of a model of Safety Governance – and the theoretical and practical tools to achieve it have been defined together with top management. The Holding Company set up a Group RSPP Coordination Committee, which meets quarterly in order to, among other things, share the results of safety performance analyses and experiences and good procedures. A special H&S Dashboard was also prepared and it has become a shared tool for the reporting of occupational health and safety performance.
THE BUSINESS MODEL
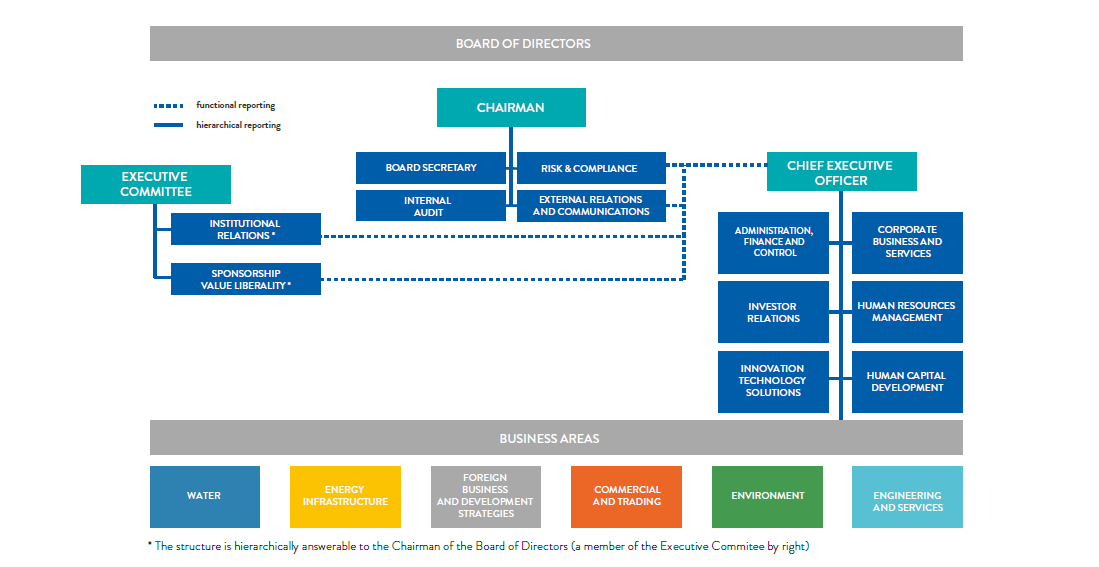
The implemented business model (chart no. 3) is based on an organizational structure wherein the Holding performs the role of steering and coordination of the Companies that make up the Group. Moreover, Acea SpA offers managerial support by means of management and legal, logistic, technical, financial and administrative services. Acea SpA’s organizational macrostructure consists of corporate functions and industrial segments to which the operating companies report (see chart no. 4).
CHART NO. 3 – ACEA’S BUSINESS MODEL
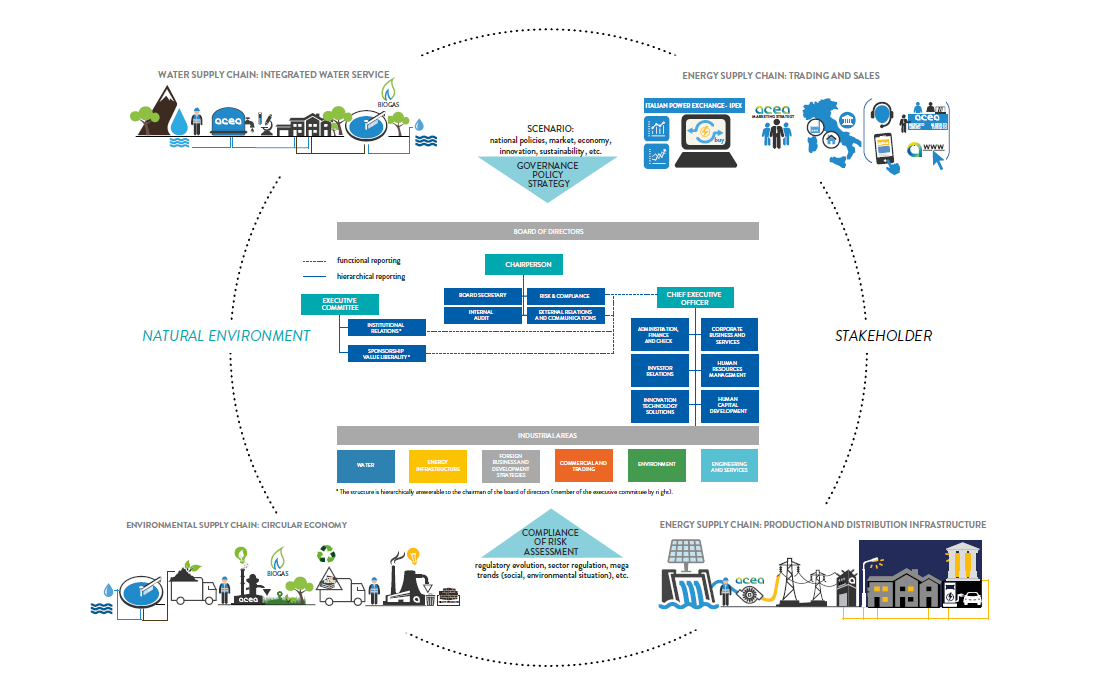
CHART NO. 4 – ACEA SPA ORGANISATION CHART AS AT 31.12.2019
Through Companies that it has equity investments in and for which it plays the role of industrial entity of reference, the Acea Group is involved in the 4 chains of activities already mentioned and shown below. The business activities are broken down in the strategic Plan (see the section titled Integrated strategy reading), which defines corporate development guidelines based on the assessments of opportunities offered by the market, the regulatory and social context of reference, the governance system and a careful identification and weighting of the risks that can impede the achievement of the goals. When performing activities and supplying services, Acea Group pays the greatest attention to its interactions with the natural environment and relations with stakeholders, thus managing the corporate activities in a manner that is consistent with the principles of sustainable development.
WATER SUPPLY CHAIN: INTEGRATED WATER SERVICE
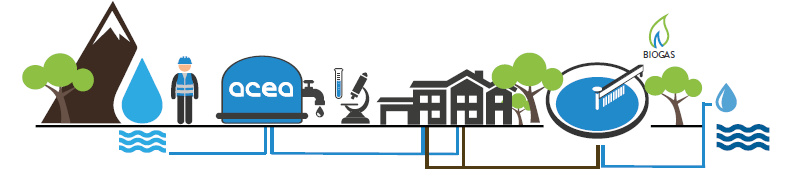
The water supply chain: starting from a careful analysis of springs and groundwater and the potential impacts of operational processes on them – for example, by defining and monitoring water districts and preparing water balances – Acea checks and guarantees the quality of water during collection and distribution in compliance with the regulatory standards envisaged for end uses. The same care is devoted to wastewater and advanced treatment phases to recover useful material and return the resource to the environment in the best possible conditions for its natural cycle to resume.
ENERGY SUPPLY CHAIN: PRODUCTION AND DISTRIBUTION INFRASTRUCTURE

Production and distribution of electricity: Acea produces energy at hydroelectric plants, waste-to-energy plants, thermoelectric plants (high-efficiency cogeneration), anaerobic digestion plants (biogas) and photovoltaic plants, for a total generation from renewable sources of about 70%. Users receive electricity thanks to the distribution grid managed and developed by Acea. The digital and innovative development in the services, stimulated and required by a constantly evolving market, commits the Distributor to tend towards smart city solutions. This is accompanied by a resilient management of the networks by which it is possible to support a future shift and increase in the uses of the electrical vector.
ENERGY SUPPLY CHAIN: TRADING AND SALES

Sale of energy and gas: the purchase of commodities (energy and gas) takes place by means of bilateral contracts or exchanges on market platforms (Electronic stock exchange) where Acea Energia supplies itself in order to resupply clients according to its respective commercial policies. The Company develops relations with the customers, based on their type, by means of increasingly more innovative and digital contact channels, however retaining traditional tools such as the telephone and public counters. The promotion of its products takes place through pull channels (shop, website, branches) as well as through sales agencies that are selected, trained and their commercial procedures monitore.
ENVIRONMENTAL SUPPLY CHAIN: CIRCULAR ECONOMY

Waste valorization and circular economy: the environmental supply chain has as its objective the valorization of waste through the reduction of volumes, their treatment, conversion into biogas, transformation into compost for agriculture and floriculture and recycling into material that is reusable in production processes. In particular, with a view to circular economy, Acea exploits the integration into water activities to recover sludge from water purification and send it for treatment to become compost, also committing itself to the growth of its market position and operational capacity through plant acquisition and development projects.